
Depending on the part that has failed, driving the vehicle for any lengthy period may cause additional internal engine problems. The timing chain may have issues with guides or tensioners, leading to engine damage if the valves hit the pistons. This particular OBD-II trouble code is deemed to be severe as your camshaft and crankshaft aren’t lining up correctly. In addition, the crankshaft position sensor is to be found on the fuel pump on some diesel applications, the flexplate/flywheel, or the crankshaft pulley (or harmonic balancer as it’s also known).
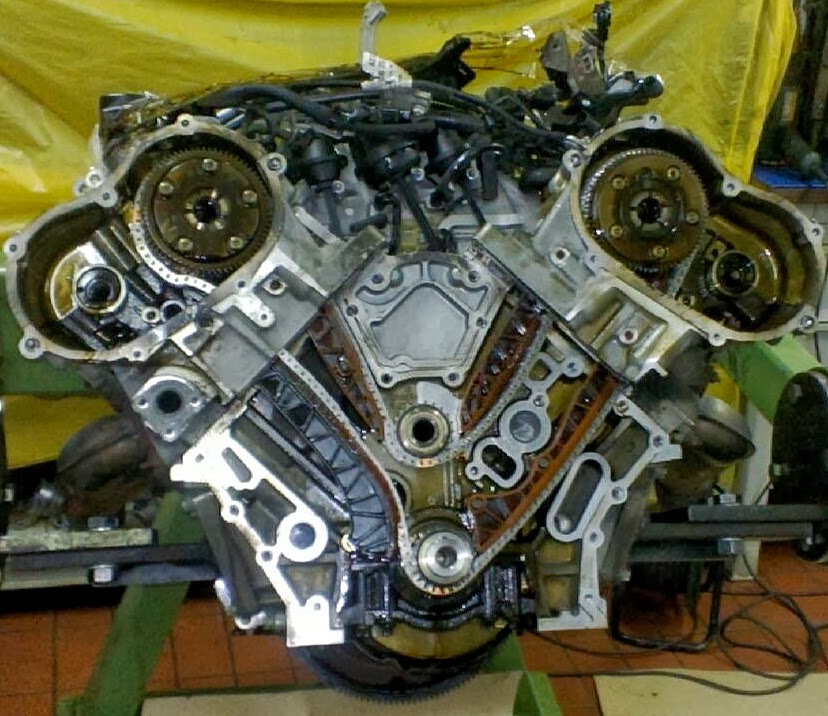

On most vehicle applications, the camshaft position sensor is located near the cylinder head so that the CMP is opposite the timing rotor attached to the engine camshaft. Unfortunately, when the signal from either the CMP or CKP sensors is incorrect or defective, the PCM simply can’t efficiently manage engine timing leading to startup problems and idling issues. The CKP relays crankshaft position and engine RPM to the PCM, and again, the data is used by the PCM to control ignition timing and fuel injection.
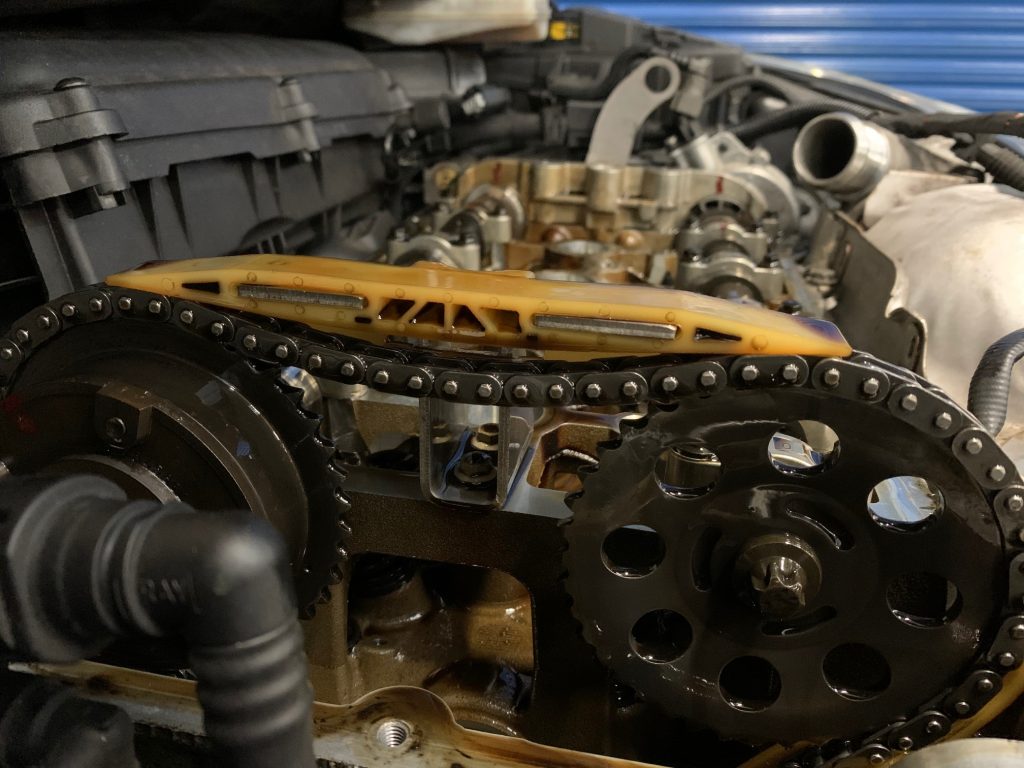
The PCM uses that data to control the fuel injectors for ignition timing to keep cylinders firing efficiently. The CMP relays the information to the vehicle’s Powertrain Control Module (PCM). When a P0016 OBD-II generic code is triggered, it alerts the driver that the camshaft position sensor (CMP) for bank 1, which detects camshaft rotation, is not corresponding to the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) signal. Tips to avoid a P0016 trouble code in future?.

What are the causes of a P0016 OBD-II code?.What are the common symptoms of a P0016 trouble code?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
